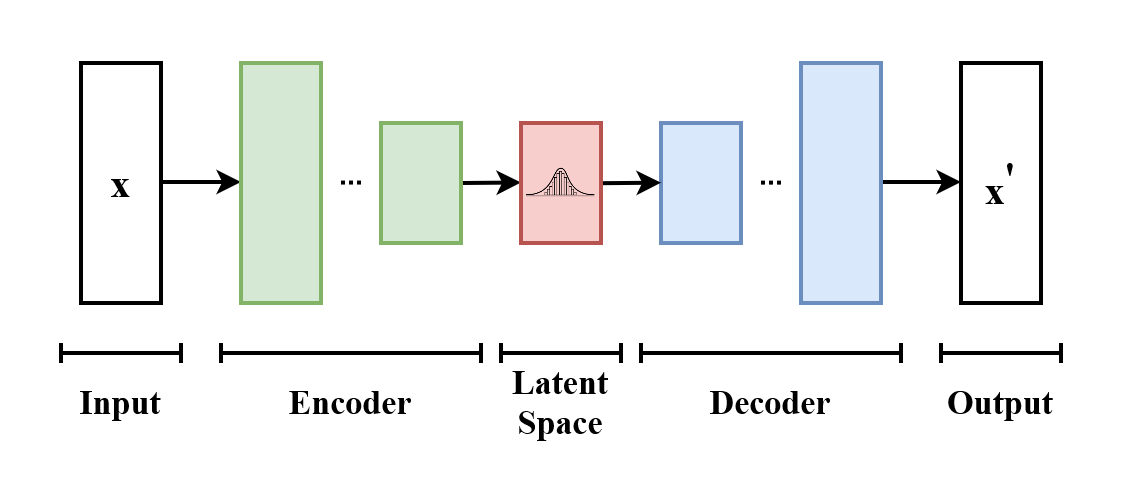
Autoencoder
Autoencoder is a neural network mainly used to discover and learn features from unlabeled data.
An autoencoder has two main part:
- Encoder: compress input data into a latent space
- Decoder: reconstruct data from the latent space as close as possible from the input
The goal is to minimise (with a loss function) the difference between the input and the output.
Applications
- Dimensionality reduction: output as close as possible as the input
- Denoising: model is trained on a clean input data. Similar noisy data is given as in input
- Anomaly detection: as denoising. The difference between (faulty) input data and reconstructed data is used as a score/threshold to detect anomalies
Variations
VAE
In a Variational Autoencoder (VAE), the latent space is composed of a mixture of distributions instead of fixed vectors.
The outputs are probabilistic, unlike traditional autoencoders, which produce deterministic reconstructions of the input. This characteristic enables the generation of diverse samples and provides control over the outputs by manipulating the parameters of the latent distribution.
Like other variational methods, the optimization objective is the Evidence Lower BOund (ELBO), which determine how generated data
Resources
- arXiv:1906.02691 – An Introduction to Variational Autoencoders