CSS
CSS is a stylesheet language. It is basically the cosmetic layer of a web page (i.e. HTML).
Variables
:root {
--main-color: blue;
}
body {
color: var(--main-color);
}@property can define variables with more precisions
Colors
Key terms
<named-color> Examples: red, green, blue
<hex-color> Examples: #FF0000, #008000, #0000FF
- Some hex codes can be shorten:
#FF000→#F00
rgb() Examples: rgb(255,0,0), rgb(0,255,0), rgb(0,0,100%)
- Values by Red-Green-Blue canals
hsl() Examples: hsl(0, 100%, 50%), hsl(120, 100%, 25%), hsl(240, 100%, 50%)
- Values define respectively the hue, saturation and lightness
- Use
hsl(120, 100%, 25%, 0.6)to apply opacity (alpha canal). Also works with % value degandturncan be used for hue value, according to the color wheel
currentColor Example: color: red; border: 1px solid currentColor;
- This special keyword can get the value defined in
color
Other specifics terms
color-mix(): mix 2 colors together (example)hwb(): define hue, whitness and blackness.oklch(): define lightness, chroma, hue (improved version oflch())color(): change the current color space (can be be detected viacolor-gamut)
Read more
- Web colors – Wikipedia
- htmlcolorcodes.com
Relative colors
The relative color syntax allows a color to be defined relative to another color
#left-square { background-color: red; }
#right-square { background-color: rgb(from red 200 g b); }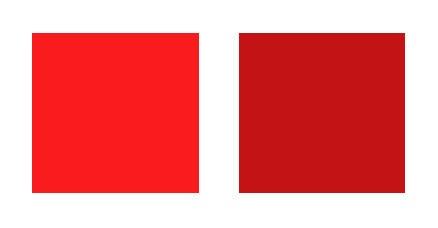
- Here,
red, which value isrgb(255, 0, 0), has been defined asrgb(200, 0, 0). The second red square has a darker tone relative to the first one. - It's possible to use other color properties in the same fashion:
color(),hsl(), etc.
Light-dark themes
You can usecolor-scheme and light-dark() to easily define light-dark color themes.
/* Use at property level */
:root {
color-scheme: light dark;
--color-background: light-dark(white, black);
}
/* Use at media query level */
@media (prefers-color-scheme: light) {
body {
color: black;
}
}INFO
You can switch between themes with @matchMedia
if (window.matchMedia && window.matchMedia('(prefers-color-scheme: dark)').matches) { /* … */ }
// Watch for change
window.matchMedia('(prefers-color-scheme: dark)').addEventListener('change', event => {
const newColorScheme = event.matches ? "dark" : "light";
});Read more: @matchMedia
Scroll
The scroll-snap properties allows to align ("snap") the scroll on certain elements within HTML containers.
.container {
scroll-snap-type: y mandatory;
scroll-padding: 50px;
scroll-margin: 50px;
}
.container .section {
scroll-snap-align: start;
}scroll-snap-type's first parameter is the axis. Second one can bemandatory(always snap to sections) orproximity(snap if close to the section).scroll-marginandscroll-paddingdefine offsets of section's align point.scroll-snap-aligncan be at thestartor at theendof the section.
Resources
- postcss.org – Tool to lint and enable extra features to CSS
- cssdb.org – A list of current and potential future CSS features
- projectwallace.com – CSS analyser